A debilitating and life-changing condition
.
About neurofibromatosis type 1 with plexiform neurofibromas (NF1-PN)
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is an incurable genetic condition caused by loss-of-function variants in the NF1 tumor-suppressor gene1-4
- Nonmalignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors called plexiform neurofibromas (PNs) are a common clinical manifestation of NF11
Up to 50%
of children and adults with NF1 develop PNs1,5,6
There are 30,000 to 50,000 people in the US living with NF1-PN, and the majority of them are adults1,5-8
NF1-PN can be associated with significant physical morbidities6,9-11
Pain
Impaired mobility
Changes in
appearance
Compression of
internal organs
- Two of the most frequently reported concerns for patients across all age groups are pain and changes in appearance12,*
- For children and adolescents, pain has been found to significantly impact their lives, even when pain medications are used13,†
- Patients with NF1 have an 8% to 16% lifetime risk of PNs transforming into malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors14,15
See how invasive and unpredictable PNs can be for people with NF15,9,16-22
- PNs can grow anywhere on the body except for the central nervous system; the most common location is the head and neck area, followed by the extremities and trunk5,9,16,17
- PNs can grow at an unpredictable rate, and there may be periods of rapid growth followed by periods of relative inactivity18-21
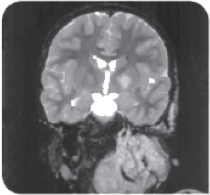
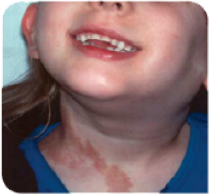
7-year-old girl with a large PN on her neck. Imagery adapted from Wise et al, 2005.22
*Based on a qualitative study in which clinicians (n=8), NF1-PN patients aged 5 years and older (n=31), and parents of NF1-PN patients aged 5 to 17 years (n=17) were interviewed for the purpose of determining which PN-related symptoms and concerns should be considered the most important to assess.12
†Based on a questionnaire completed by the caregivers of 59 NF1-PN patients, 6 to 18 years of age, and 41 NF1-PN patients, 10 to 18 years of age, who were enrolled in an NF1 natural history study at the National Cancer Institute.13
Surgery to manage NF1-PN is not always feasible and outcomes can be variable
- Debulking surgery may be considered for large PNs that are interfering with vital structures, including the airway or spinal cord, or for PNs that could lead to functional decline or changes in appearance23,24
- However, the feasibility of surgery can be restricted by tumor site or infiltration of surrounding nerves and vasculature25
Up to ~85% of PNs
are not amenable to complete resection1,25,2623% of PNs
regrow after a complete resection27,‡- In a survey, 16% (5/32) of patients with NF1-PN who received debulking surgery reported complications11,§
- Of the patients assessed for surgical complications associated with debulking surgery, 9% (3/32) experienced acute surgical complications, including delayed healing and bleeding, and 6% (2/32) experienced chronic postoperative symptoms, such as functional impairment and nerve damage
- In a retrospective analysis, lasting postoperative complications were seen in 18% (17/96) of patients5,||
‡Based on a retrospective analysis of clinical and MRI data of 52 children and adults with NF1 who had surgery to remove PNs at a referral center in Germany.27
§Based on a cross-sectional study using a one-time survey of NF1-PN patients and caregivers. Sixty-one pediatric patients 8 to 18 years old and their caregivers, and 21 additional caregivers of patients 2 to 7 years old (total of 82 caregivers) participated in the survey.11
∥Based on a retrospective analysis of 96 children with NF1 who had PN surgery at a single center located in the US.5
Clinical management of NF1-PN
Clinical management of NF1-PN
Drs. Nghiemphu and Moertel discuss the unmet needs and challenges in managing patients with NF1-PN and factors to consider when determining treatment options.
GOMEKLI logo.
Episode #1: Clinical Management of NF1-PN
The first FDA-approved treatment for both adult and pediatric patients aged ≥2 years with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN) not amenable to complete resection.
[Dr Nghiemphu]
My name is Dr Phioanh Leia Nghiemphu, and I'm a neuro-oncologist and the director of the UCLA Neurofibromatosis and Schwannomatosis Clinic.
I'm happy to share today that I also have Dr Moertel, one of the lead investigators of the ReNeu study.
[Dr Moertel]
My name is Dr Christopher Moertel.
I'm a neuro-oncologist and I serve as professor of pediatrics at the University of Minnesota School of Medicine, and I'm the medical director of the Comprehensive Neurofibromatosis Clinic at the University of Minnesota Masonic Children's Hospital.
[Dr Nghiemphu]
I'd like to have a brief discussion with Dr Moertel about unmet needs and the clinical management of NF1-PN in our practices.
How we treat symptomatic patients with NF1-PN is always evolving. So, in your opinion, Dr Moertel, what factors are the most important when determining management options for a patient with NF1-PN that is symptomatic and has been deemed in need of intervention?
Do these factors differ between pediatric and adult patients? And, if yes, how do they differ?
[Dr Moertel]
Determining the management of patients with NF1-PN is multifactorial, as you know, as it involves considerations of several treatment options to reduce or prevent the morbidities associated with PNs.
When deciding whether or not surgery is appropriate, factors that should be considered include the size and location of the tumor and amenability to resection.
Up to approximately 85% of PNs are not amenable to complete resection.
Additionally, many patients experience postoperative tumor regrowth, pain, and complications of the surgery.
When selecting a systemic treatment, contraindications or preexisting conditions, the age of the patient, and a patient's ability to swallow pills are considerations.
[Dr Nghiemphu]
What are some of the challenges in managing this disease in your patients?
[Dr Moertel]
Well, as we just mentioned, the rate of PN regrowth after partial, or even complete, resection is one of the many challenges of surgery.
[Dr Moertel, voiceover only]
For systemic treatment, until now, there was no FDA-approved option to treat adult patients with NF1-PN or for individuals who have difficulty swallowing intact capsules. And that's a lot of people in my practice.
Until now, treatment options for adults were limited to surgery or off-label therapies.
[Dr Moertel]
Having an FDA-approved treatment option for adults is a great step forward.
Dr Nghiemphu, is it important to address the symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas in a timely manner? And, if so, can you explain why it's important?
[Dr Nghiemphu]
Yes, the clinical manifestation of NF1 can start soon after birth and continue throughout childhood and adulthood.
These manifestations can affect the skeletal system, the skin, and the central nervous system. And NF1-PNs, which can occur at any time throughout life, can be debilitating.
[Dr Nghiemphu, voiceover only]
They are associated with significant morbidities, such as pain, disfigurement, compression of internal organs, and impaired physical function.
The most rapid growth of NF1-PNs usually occurs among those aged 5 years or younger. However, although some patients may experience slow PN regrowth, clinical morbidities often persist and can have a detrimental impact.
[Dr Moertel]
Dr Nghiemphu, of the symptoms experienced with plexiform neurofibromas that you see, what are the most common among your patients?
[Dr Nghiemphu]
For many of my patients, pain can interfere with daily functioning, and the disfigurement can have a substantial effect on their lives.
Reducing the size of PNs may help address these morbidities.
[Dr Moertel, voiceover only]
I would like to review the highlights of the Important Safety Information.
GOMEKLI can cause ocular toxicity, including retinal vein occlusion, retinal pigment epithelium detachment, and blurred vision.
Conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessments prior to initiating GOMEKLI, at regular intervals during treatment, and to evaluate any new or worsening visual changes.
Follow the dose modification or discontinuation guidance from the Prescribing Information as needed.
GOMEKLI can cause left ventricular dysfunction.
It can occur in patients who are treated with GOMEKLI.
Before initiating GOMEKLI, assess ejection fraction by echocardiogram and monitor ejection fraction every 3 months during the first year and then as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce the dose of, or discontinue GOMEKLI, depending on the severity of the adverse reaction.
GOMEKLI can cause dermatologic adverse reactions, including rash.
The most frequent rashes include dermatitis acneiform, rash, eczema, maculo-papular rash, and pustular rash.
Initiate supportive care at first signs of dermatologic adverse reactions and follow the dose modification or discontinuation guidance from the Prescribing Information as needed.
GOMEKLI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman.
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of GOMEKLI.
Because of the potential for adverse reactions in breastfed children, women should be advised not to breastfeed during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 1 week after the last dose.
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 6 weeks after the last dose.
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 3 months after the last dose of GOMEKLI.
Drs. Nghiemphu and Moertel discuss the unmet needs and challenges in managing patients with NF1-PN and factors to consider when determining treatment options.
Indication
GOMEKLI (mirdametinib) is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN) not amenable to complete resection.
Important Safety Information
Warnings and Precautions
Ocular Toxicity: GOMEKLI can cause ocular toxicity including retinal vein occlusion (RVO), retinal pigment epithelium detachment (RPED), and blurred vision. In the adult pooled safety population, ocular toxicity occurred in 28% of patients treated with GOMEKLI: 21% were Grade 1, 5% were Grade 2 and 1.3% were Grade 3. RVO occurred in 2.7%, RPED occurred in 1.3%, and blurred vision occurred in 9% of adult patients. In the pediatric pooled safety population, ocular toxicity occurred in 19% of patients: 17% were Grade 1 and 1.7% were Grade 2. Conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessments prior to initiating GOMEKLI, at regular intervals during treatment, and to evaluate any new or worsening visual changes such as blurred vision. Continue, withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI as clinically indicated.
Left Ventricular Dysfunction: GOMEKLI can cause left ventricular dysfunction. GOMEKLI has not been studied in patients with a history of clinically significant cardiac disease or LVEF <55% prior to initiation of treatment. In the ReNeu study, decreased LVEF of 10 to <20% occurred in 16% of adult patients treated with GOMEKLI. Five patients (9%) required dose interruption, one patient (1.7%) required a dose reduction, and one patient required permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI. The median time to first onset of decreased LVEF in adult patients was 70 days. Decreased LVEF of 10 to <20% occurred in 25%, and decreased LVEF of ≥20% occurred in 1.8% of pediatric patients treated with GOMEKLI. One patient (1.8%) required dose interruption of GOMEKLI. The median time to first onset of decreased LVEF in pediatric patients was 132 days. All patients with decreased LVEF were identified during routine echocardiography, and decreased LVEF resolved in 75% of patients. Before initiating GOMEKLI, assess ejection fraction (EF) by echocardiogram. Monitor EF every 3 months during the first year and then as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity of adverse reaction.
Dermatologic Adverse Reactions: GOMEKLI can cause dermatologic adverse reactions including rash. The most frequent rashes included dermatitis acneiform, rash, eczema, maculo-papular rash and pustular rash. In the pooled adult safety population, rash occurred in 92% of patients treated with GOMEKLI (37% were Grade 2 and 8% were Grade 3) and resulted in permanent discontinuation in 11% of patients. In the pooled pediatric safety population, rash occurred in 72% of patients treated with GOMEKLI (22% were Grade 2 and 3.4% were Grade 3) and resulted in permanent discontinuation in 3.4% of patients. Initiate supportive care at first signs of dermatologic adverse reactions. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity of adverse reaction.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: GOMEKLI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of GOMEKLI. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Also advise patients to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 6 weeks after the last dose (females) or 3 months after the last dose (males).Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (>25%) in adult patients were rash (90%), diarrhea (59%), nausea (52%), musculoskeletal pain (41%), vomiting (38%), and fatigue (29%). Serious adverse reactions occurred in 17% of adult patients who received GOMEKLI. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormality (>2%) was increased creatine phosphokinase.
The most common adverse reactions (>25%) in pediatric patients were rash (73%), diarrhea (55%), musculoskeletal pain (41%), abdominal pain (39%), vomiting (39%), headache (34%), paronychia (32%), left ventricular dysfunction (27%), and nausea (27%). Serious adverse reactions occurred in 14% of pediatric patients who received GOMEKLI. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (>2%) were decreased neutrophil count and increased creatine phosphokinase.Use in Specific Populations
Indication
References
- Ejerskov C, Farholt S, Nielsen FSK, et al. Clinical characteristics and management of children and adults with neurofibromatosis type 1 and plexiform neurofibromas in Denmark: a nationwide study. Oncol Ther. 2023;11(1):97-110.
- Lee T-SJ, Chopra M, Kim RH, Parkin PC, Barnett-Tapia C. Incidence and prevalence of neurofibromatosis type 1 and 2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2023;18(1):292.
- Tamura R. Current understanding of neurofibromatosis type 1, 2, and schwannomatosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5850.
- Yap Y-S, McPherson JR, Ong C-K, et al. The NF1 gene revisited – from bench to bedside. Oncotarget. 2014;5(15):5873-5892.
- Prada CE, Rangwala FA, Martin LJ, et al. Pediatric plexiform neurofibromas: impact on morbidity and mortality in neurofibromatosis type 1. J Pediatr. 2012;160(3):461-467.
- Miller DT, Freedenberg D, Schorry E, Ullrich NJ, Viskochil D, Korf BR; Council on Genetics; American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Health supervision for children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Pediatrics. 2019;143(5):e20190660.
- Kallionpää RA, Uusitalo E, Leppävirta J, Pöyhönen M, Peltonen S, Peltonen J. Prevalence of neurofibromatosis type 1 in the Finnish population. Genet Med. 2018;20(9):1082-1086.
- U.S. population estimated at 332,403,650 on Jan. 1, 2022. U.S. Department of Commerce. January 6, 2022. Accessed April 16, 2024. https://www.commerce.gov/news/blog/2022/01/us-population-estimated-332403650-jan-1-2022
- Darrigo LG Jr, Ferraz VEF, Cormedi MCV, et al. Epidemiological profile and clinical characteristics of 491 Brazilian patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Brain Behav. 2022;12(6):e2599.
- Gross AM, Singh G, Akshintala S, et al. Association of plexiform neurofibroma volume changes and development of clinical morbidities in neurofibromatosis 1. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(12):1643-1651.
- Yang X, Yoo HK, Amin S, et al. Clinical and humanistic burden among pediatric patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 and plexiform neurofibroma in the USA. Childs Nerv Syst. 2022;38(8):1513-1522.
- Lai J-S, Jensen SE, Patel ZS, Listernick R, Charrow J. Using a qualitative approach to conceptualize concerns of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 associated plexiform neurofibromas (pNF) across the lifespan. Am J Med Genet A. 2017;173(1):79-87.
- Wolters PL, Burns KM, Martin S, et al. Pain interference in youth with neurofibromatosis type 1 and plexiform neurofibromas and relation to disease severity, social-emotional functioning, and quality of life. Am J Med Genet A. 2015;167A(9):2103-2113.
- Higham CS, Dombi E, Rogiers A, et al. The characteristics of 76 atypical neurofibromas as precursors to neurofibromatosis 1 associated malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2018;20(6):818-825.
- Miettinen MM, Antonescu CR, Fletcher CDM, et al. Histopathologic evaluation of atypical neurofibromatous tumors and their transformation into malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor in patients with neurofibromatosis 1—a consensus overview. Hum Pathol. 2017;67:1-10.
- Plotkin SR, Bredella MA, Cai W, et al. Quantitative assessment of whole-body tumor burden in adult patients with neurofibromatosis. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35711.
- Nguyen R, Kluwe L, Fuensterer C, Kentsch M, Friedrich RE, Mautner V-F. Plexiform neurofibromas in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: frequency and associated clinical deficits. J Pediatr. 2011;159(4):652–655.e2.
- Ferner RE, Huson SM, Thomas N, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of individuals with neurofibromatosis 1. J Med Genet. 2007;44(2):81-88.
- Akshintala S, Baldwin A, Liewehr DJ, et al. Longitudinal evaluation of peripheral nerve sheath tumors in neurofibromatosis type 1: growth analysis of plexiform neurofibromas and distinct nodular lesions. Neuro Oncol. 2020;22(9):1368-1378.
- Ly KI, Merker VL, Cai W, et al. Ten-year follow-up of internal neurofibroma growth behavior in adult patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 using whole-body MRI. Neurology. 2023;100(7):e661-e670.
- Nguyen R, Dombi E, Widemann BC, et al. Growth dynamics of plexiform neurofibromas: a retrospective cohort study of 201 patients with neurofibromatosis 1. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012:7:75.
- Wise JB, Cryer JE, Belasco JB, Jacobs I, Elden L. Management of head and neck plexiform neurofibromas in pediatric patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2005;131(8):712-718.
- Fisher MJ, Blakeley JO, Weiss BD, et al. Management of neurofibromatosis type 1-associated plexiform neurofibromas. Neuro Oncol. 2022;24(11):1827-1844.
- Armstrong AE, Belzberg AJ, Crawford JR, Hirbe AC, Wang ZJ. Treatment decisions and the use of MEK inhibitors for children with neurofibromatosis type 1-related plexiform neurofibromas. BMC Cancer. 2023;23(1):553.
- Needle MN, Cnaan A, Dattilo J, et al. Prognostic signs in the surgical management of plexiform neurofibroma: the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia experience, 1974-1994. J Pediatr. 1997;131(5):678-682.
- Wolkenstein P, Chaix Y, Entz Werle N, et al. French cohort of children and adolescents with neurofibromatosis type 1 and symptomatic inoperable plexiform neurofibromas: CASSIOPEA study. Eur J Med Genet. 2023; 66(5):104734.
- Nguyen R, Ibrahim C, Friedrich RE, Westphal M, Schuhmann M, Mautner V-F. Growth behavior of plexiform neurofibromas after surgery. Genet Med. 2013;15(9):691-697.
- GOMEKLI. Prescribing Information. SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.
- Cheng Y, Tian H. Current development status of MEK inhibitors. Molecules. 2017;22(10):1551.