GOMEKLI (mirdametinib) has proven results in children and adolescents with NF1-PN*

Primary analysis
GOMEKLI shrank plexiform neurofibromas (PNs) in pediatric patients1
Primary endpoint: confirmed overall response rate (ORR)1,†
achieved a confirmed response‡
(≥20% reduction in PN volume on consecutive scans)(95% CI: 38-65)
Of the patients with a confirmed response:
had a deep response
(>50% reduction in PN volume)2
(This analysis was post hoc and exploratory)
In a post hoc subgroup analysis:
Patients who achieved a deep response had a longer duration of treatment than those who did not3
The median duration of treatment for patients with a deep response was 27 months (range: 22 to 39 months) vs 25 months (range: 12 to 40 months) for those with a 20% to 50% reduction in PN volume.
Learn more about the depth of response achieved by children and adolescents in ReNeu.
†Confirmed ORR defined as the proportion of patients with complete response (disappearance of the target PN) or partial response (≥20% reduction) on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the target PN volume from baseline to Cycle 24 (treatment phase) as assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR) on ≥2 consecutive scans within 2 to 6 months.1
‡All partial responses.1
Getting patients started
Getting patients started
Drs. Nghiemphu and Weintraub discuss how to work with patients to set up a positive treatment experience with GOMEKLI.
[Title builds on purple background with GOMEKLI logo in top right corner.]
Text onscreen:
Chapter 1: Setting efficacy expectations
Voice-over:
Dr. Nghiemphu: Hello. I’m Dr. Phioanh Leia Nghiemphu, a neuro-oncologist specializing in neurofibromatosis and brain tumors in adults.
Text onscreen:
Phioanh Leia Nghiemphu, MD
Dr. Weintraub: And I’m Dr. Lauren Weintraub, a hematologist and oncologist specializing in pediatric cancers and blood disorders. In this video, we’ll talk about how to support a positive treatment experience for patients taking GOMEKLI.
Text onscreen:
Lauren Weintraub, MD
GOMEKLI is the first FDA-approved treatment for both adults and children 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 who have symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas that are not amenable to complete resection. Important Safety Information for GOMEKLI will be presented later in this video.
Text onscreen:
GOMEKLI is the first FDA-approved treatment for both adults and children 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN) that are not amenable to complete resection.
Voice-over:
Dr. Nghiemphu: Several factors can drive the decision to use a systemic therapy. I consider how the plexiform neurofibromas are impacting my patient: Are they in pain? Is the plexiform neurofibroma causing changes in appearance? Has the patient’s mobility changed?
The patient and I have a conversation about their options, including surgery. For some patients, the plexiform neurofibromas are so intertwined with the nerves that complete resection is not possible. Other patients don’t want to undergo surgery. Either way, we discuss how an oral systemic treatment may be appropriate.
Voice-over: When discussing GOMEKLI as an option for patients, I like to go over some of the results from the phase 2b, single-arm ReNeu trial. The data can be complex, so I focus on explaining it in a way that’s clear and relatable. I mention that both adults and children with NF1-PN were included, that they received GOMEKLI for about 2 years, and that they had the option to remain on GOMEKLI for long-term follow-up.
Text onscreen:
114 patients
58 adult patients (18 to 69 years)
56 pediatric patients (2 to 17 years)
Voice-over:
Dr. Weintraub: The primary endpoint was confirmed overall response rate, and I explain that a confirmed overall response meant a person treated with GOMEKLI had 2 or more consecutive MRI scans showing that their plexiform shrank by 20% or more.
Text onscreen:
Primary endpoint
Confirmed overall response (ORR), defined as the proportion of patients with complete response (disappearance of the target PN) or partial response (≥20% reduction) on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the target PN volume from baseline to Cycle 24 (treatment phase) as assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR) on ≥2 consecutive scans within 2 to 6 months.
Voice-over:
Dr. Weintraub: I also note that secondary endpoints included duration of response and change in patient-reported outcomes of tumor pain severity, pain interference, and health-related quality of life.
In the ReNeu clinical trial, 41% of adult patients—or 24 out of 58—saw their plexiform neurofibroma shrink by at least 20%. Of these 24 patients, 62% achieved a deep response, meaning their target plexiform neurofibroma decreased by more than half the size it was at baseline.
Text onscreen:
Graphic of confirmed overall response rates in adults.
Voice-over:
Dr. Weintraub: In the pediatric cohort, 52% of patients—or 29 out of 56—achieved a confirmed overall response. Of these 29 patients, more than half—52%—achieved a deep response.
Text onscreen:
Graphic of confirmed overall response rates in children.
Voice-over:
Dr. Weintraub: I think it’s important to set realistic expectations about how GOMEKLI may help, so I tailor the conversation to the individual characteristics and needs of the patient. I also underscore that not everyone will have the same results.
Dr. Nghiemphu: Yeah, it’s so important to remind patients that clinical trial data in the aggregate is one thing and their personal experience on treatment is another. If patients are expecting to see their plexiform neurofibroma get smaller overnight or in a week, they could get discouraged when that doesn’t happen and want to stop taking their medication. That’s definitely something I want to get ahead of before they start treatment. I highlight that while some patients in the ReNeu trial started to see their plexiform neurofibromas shrink within about 4 months of starting GOMEKLI, for others it took longer. For some it took about 8 months or longer to see a 20% or greater reduction on back-to-back MRI scans. But it’s important that patients stay on track and keep taking their medication as prescribed so that they can get the most out of their treatment.
Dr. Weintraub: That’s a great point. Speaking of staying on track, one question that frequently comes up in my conversations with caregivers is how long their child will have to stay on treatment. I tell them that while every patient is unique, I've had a number of patients who participated in the ReNeu trial and have remained on GOMEKLI treatment ever since.
Text onscreen:
GOMEKLI treatment should be continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Text onscreen:
Chapter 2: Reviewing adverse reactions
Text onscreen:
Dr. Phioanh Leia Nghiemphu and Dr. Lauren Weintraub sitting in chairs
Voice-over:
Dr. Nghiemphu: Explaining side effects is a critical part of the initial treatment conversation. I don’t want to overwhelm patients, but I certainly want them to understand what changes, aside from changes in the size of their plexiform neurofibromas, they may experience.
In ReNeu, the most commonly reported adverse reactions in both adults and children were rash, diarrhea, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, and vomiting. Fatigue was also reported in adults.
Image onscreen:
Chart with adult adverse reaction data
Voice-over:
Dr. Nghiemphu: Abdominal pain, headache, paronychia, and left ventricular dysfunction were also reported in children. The most common severe lab abnormalities were increased creatine phosphokinase, or CPK, in both adults and children and decreased neutrophil count in children. Serious side effects associated with GOMEKLI include eye problems, heart problems, skin problems, and embryo-fetal toxicity.
Image onscreen:
Chart with pediatric adverse reaction data
Voice-over:
Dr. Weintraub: I feel it's important to set expectations with patients and caregivers regarding skin-related side effects and counsel them on management strategies. It’s important to address any concerns they may have before starting treatment. Trust me, no teenager wants to be dealing with skin issues on top of living with plexiform neurofibromas.
Dr. Nghiemphu: I definitely have similar conversations with my adult patients about the potential skin-related and gastrointestinal side effects they may experience while on GOMEKLI.
Text onscreen:
Of the patients who had dermatologic adverse reactions in ReNeu, the majority (80%) experienced first onset during Cycle 1 of treatment.
Voice-over:
Dr. Nghiemphu: I make sure they understand that many of these side effects were seen early in the course of treatment and that there are ways to help manage them, including over-the-counter remedies, medications, and even small lifestyle changes.
Text onscreen:
Of the patients who had GI adverse reactions in ReNeu, the majority experienced first onset early (Cycles 1-3).
Text onscreen:
Chart detailing the proportion of patients experiencing GI reactions in the first 2 cycles of GOMEKLI treatment.
Voice-over:
Dr. Nghiemphu: I also discuss how important it is that they are proactive and let me know right away if something is going on. The earlier we can treat the side effect, the better chance we have at resolving it quickly. In addition to managing the side effects, it’s important for patients and caregivers to know that interrupting or reducing their GOMEKLI dose is also an option. And if side effects continue after those adjustments, we have the option to permanently stop GOMEKLI.
Dr. Weintraub: Patients and caregivers should also know that certain assessments, like blood and urine tests, are required before and throughout GOMEKLI treatment. Additionally, because GOMEKLI may cause serious issues with the eyes and heart, eye exams and echocardiograms are also required before and throughout treatment.
Text onscreen:
Icons and check marks next to assessments: blood tests, urinalysis, eye exams, and echocardiograms
Voice-over:
Dr. Weintraub: Generally, these assessments are done more frequently at the start of treatment and become less frequent over time, as things remain stable. I think it’s important for patients and their caregivers to know that these routine assessments help me and their care team monitor how they are doing on treatment. The GOMEKLI Dosing and Adverse Reaction Management Guide outlines some steps we can take as care providers to help manage adverse reactions that occur during GOMEKLI treatment.
Text onscreen:
Animated Dosing and Adverse Reaction Management Guide and QR code.
Text onscreen:
Chapter 3: Dosing, administration, and support
Text onscreen:
Dr. Phioanh Leia Nghiemphu and Dr. Lauren Weintraub sitting in chairs
Voice-over:
Dr. Nghiemphu: How a medication is administered is usually one of the first questions patients have when we’re discussing treatment. GOMEKLI is a twice-daily oral medication that can be taken with or without food. It’s available in 2 capsule sizes and as a dispersible tablet for those who have difficulty swallowing.
Dr. Weintraub: Having the dispersible option is terrific for my patients who can’t or don’t want to take pills. I have a preteen patient who doesn’t like pills and the liquid formulation is just so much easier for him. I also know many caregivers prefer the dispersible tablet because it helps with administering the medication to younger patients.
Dr. Nghiemphu: And of course, some patients have plexiform neurofibromas in the head and neck area that can impact their ability to swallow, so having the option of a dispersible tablet is beneficial to them as well. The dosing schedule for GOMEKLI is 3 weeks on, 1 week off.
Text onscreen:
A chart showing the 4-week dosing cycle
Dr. Nghiemphu: For some patients, having that 1 week off is a nice break because they don’t have to worry about taking treatment. The GOMEKLI Digital Companion is a free and secure resource, available on the Medisafe app, that allows patients to set customized medication reminders, so they never miss a dose.
Dr. Weintraub: We know the coordination of starting a treatment can be a lot for patients and caregivers. SpringWorks CareConnections provides personalized support services to help patients get started and stay on track with GOMEKLI. This includes coverage and access support, financial assistance, personalized education, and emotional support.
Text onscreen:
SpringWorks CareConnections logo and a QR code
Dr. Weintraub: There’s also a full library of resources on GOMEKLI.com that can help set patients up for a positive treatment experience.
Text onscreen:
Additional videos and resources to support your practice and your patients are on GOMEKLI.com/hcp.
Text onscreen:
QR code
Voice-over:
Dr. Nghiemphu: I think we can all agree that when starting a new treatment, it’s important to provide patients with as much information as possible to help set them up for success.
Thank you for listening to our discussion of how we support patients when starting their treatment journey with GOMEKLI.
Voice-over:
Indication
GOMEKLI (mirdametinib) is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN) not amenable to complete resection.
Important Safety Information
Warning and Precautions
Ocular Toxicity: GOMEKLI can cause ocular toxicity including retinal vein occlusion (RVO), retinal pigment epithelium detachment (RPED), and blurred vision. In the adult pooled safety population, ocular toxicity occurred in 28% of patients treated with GOMEKLI: 21% were Grade 1, 5% were Grade 2 and 1.3% were Grade 3. RVO occurred in 2.7%, RPED occurred in 1.3%, and blurred vision occurred in 9% of adult patients. In the pediatric pooled safety population, ocular toxicity occurred in 19% of patients: 17% were Grade 1 and 1.7% were Grade 2. Conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessments prior to initiating GOMEKLI, at regular intervals during treatment, and to evaluate any new or worsening visual changes such as blurred vision. Continue, withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI as clinically indicated.
Left Ventricular Dysfunction: GOMEKLI can cause left ventricular dysfunction. GOMEKLI has not been studied in patients with a history of clinically significant cardiac disease or LVEF <55% prior to initiation of treatment. In the ReNeu study, decreased LVEF of 10 to <20% occurred in 16% of adult patients treated with GOMEKLI. Five patients (9%) required dose interruption, one patient (1.7%) required a dose reduction, and one patient required permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI. The median time to first onset of decreased LVEF in adult patients was 70 days. Decreased LVEF of 10 to <20% occurred in 25%, and decreased LVEF of ≥20% occurred in 1.8% of pediatric patients treated with GOMEKLI. One patient (1.8%) required dose interruption of GOMEKLI. The median time to first onset of decreased LVEF in pediatric patients was 132 days. All patients with decreased LVEF were identified during routine echocardiography, and decreased LVEF resolved in 75% of patients. Before initiating GOMEKLI, assess ejection fraction (EF) by echocardiogram. Monitor EF every 3 months during the first year and then as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity of adverse reaction.
Dermatologic Adverse Reactions: GOMEKLI can cause dermatologic adverse reactions including rash. The most frequent rashes included dermatitis acneiform, rash, eczema, maculo-papular rash and pustular rash. In the pooled adult safety population, rash occurred in 92% of patients treated with GOMEKLI (37% were Grade 2 and 8% were Grade 3) and resulted in permanent discontinuation in 11% of patients. In the pooled pediatric safety population, rash occurred in 72% of patients treated with GOMEKLI (22% were Grade 2 and 3.4% were Grade 3) and resulted in permanent discontinuation in 3.4% of patients. Initiate supportive care at first signs of dermatologic adverse reactions. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity of adverse reaction.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: GOMEKLI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of GOMEKLI. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Also advise patients to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 6 weeks after the last dose (females) or 3 months after the last dose (males).
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (>25%) in adult patients were rash (90%), diarrhea (59%), nausea (52%), musculoskeletal pain (41%), vomiting (38%), and fatigue (29%). Serious adverse reactions occurred in 17% of adult patients who received GOMEKLI. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormality (>2%) was increased creatine phosphokinase.
The most common adverse reactions (>25%) in pediatric patients were rash (73%), diarrhea (55%), musculoskeletal pain (41%), abdominal pain (39%), vomiting (39%), headache (34%), paronychia (32%), left ventricular dysfunction (27%), and nausea (27%). Serious adverse reactions occurred in 14% of pediatric patients who received GOMEKLI. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (>2%) were decreased neutrophil count and increased creatine phosphokinase.
Use in Specific Populations
Verify the pregnancy status of patients of reproductive potential prior to initiating GOMEKLI. Due to the potential for adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise patients not to breastfeed during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 1 week after the last dose.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact SpringWorks Therapeutics Inc. at 1-888-400-7989 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Patient Information and Instructions for Use.
Text onscreen:
GOMEKLI and SpringWorks logos
Text onscreen:
@2025 SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved. GOMEKLI and SpringWorks CareConnections are registered trademarks of SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc. C_GOM_US_0413 8/25
Drs. Nghiemphu and Weintraub discuss how to work with patients to set up a positive treatment experience with GOMEKLI.
Primary analysis
Depth of response achieved by pediatric patients2,4
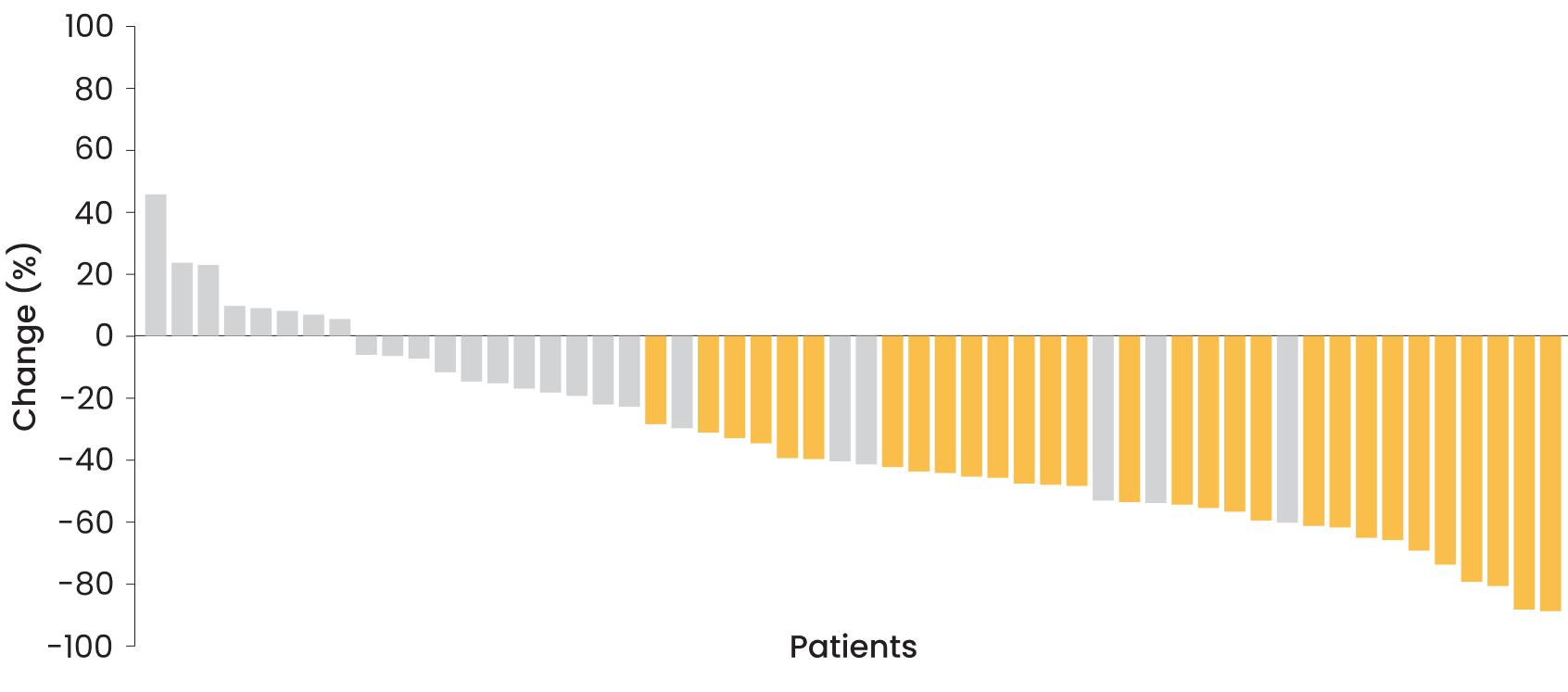
Data for 54 out of 56 patients shown here; 2 patients did not have postbaseline MRI assessments. Gold bars represent those patients who had a confirmed overall response (≥20% reduction in PN volume on consecutive MRI scans). Gray bars represent nonresponders who had a best overall response of stable disease or progressive disease.
-42%
(range: −91% to 48%)
-91%
View 2 case studies from ReNeu
ReNeu case study:
7-year-old female with neck PN2
Baseline

Cycle 21

PN with a volume of 95 mL at baseline was reduced to 48 mL (-49%) at Cycle 21.
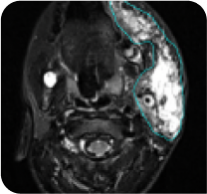
ReNeu deep response case study: 8-year-old male with head/neck PN2
Baseline
Cycle 24
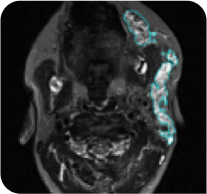
PN with a volume of 221 mL at baseline was reduced to 39 mL (-82%) at Cycle 24.
Tumor edges are indicated in cyan. Individual results may vary.

Do you have patients who are starting GOMEKLI?
Long-term data
Additional responses in pediatric patients seen over time5
The latest findings from ReNeu show that longer duration of GOMEKLI treatment improved confirmed ORR, with some deep responses achieved. Prior to data cutoff:
-
55% (31/56) of patients achieved a confirmed overall response (all partial responses)
-
61% (19/31) of those with a confirmed response achieved a deep response
-
No new safety signals emerged
Primary analysis
Durable response in pediatric patients1,2
90% (26/29) of the confirmed overall responses remained durable for ≥12 months1,§
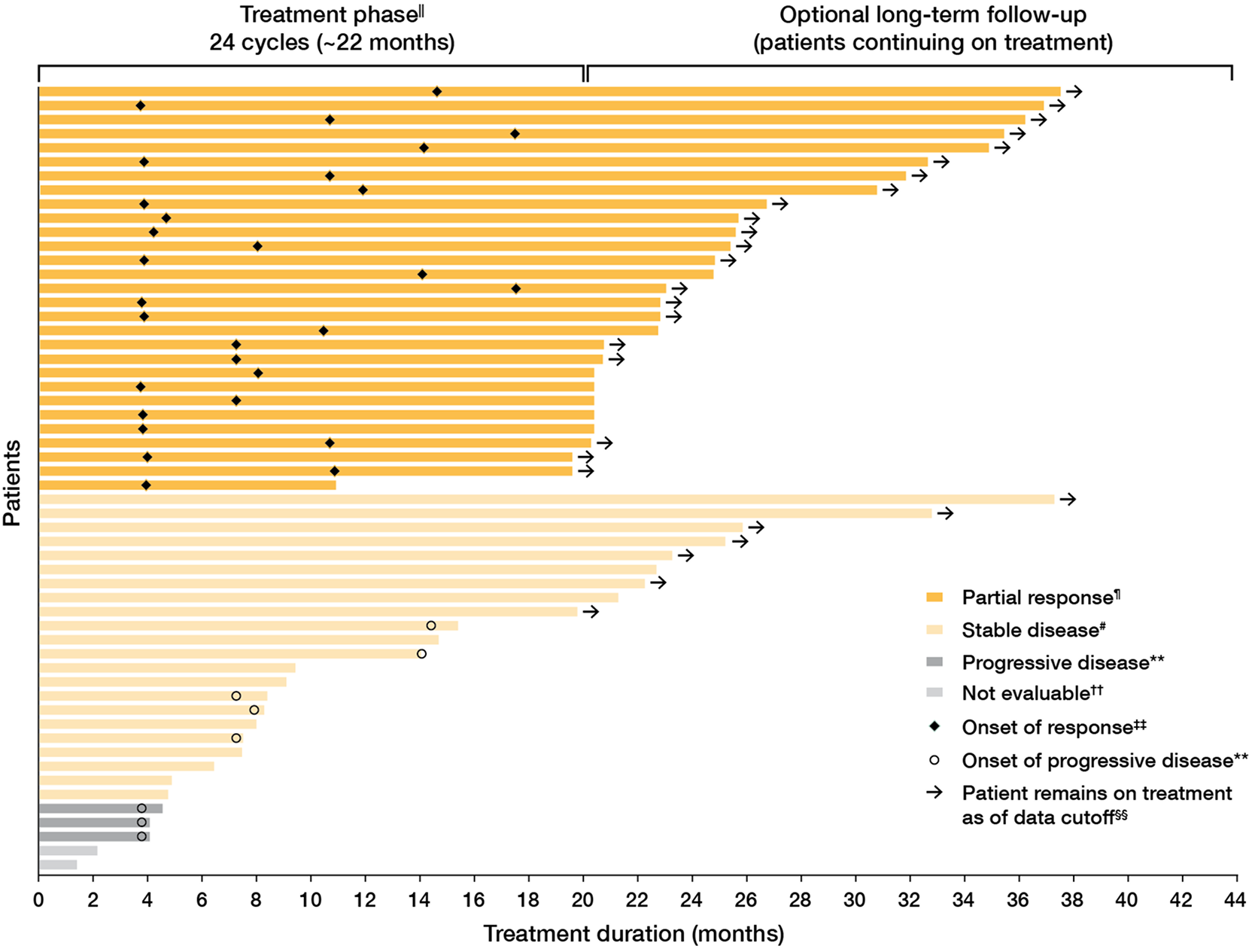
85%
of patients
of patients
(28/33) who completed the treatment phase chose to remain on GOMEKLI for long-term follow-up.2
View additional response data
Best overall response status among the 56 pediatric patients taking GOMEKLI2,4
Complete response
0 patients
29 patients
22 patients
Progressive disease**
3 patients
Not evaluable††
2 patients
- Among evaluable patients, the majority had either a partial response or stable disease based on best overall confirmed response
- 8 patients had disease progression during the treatment phase
Stable disease and progressive disease were exploratory endpoints and data should be interpreted with caution as ReNeu is a single-arm trial.
- 48% (14/29) of the confirmed overall responses remained durable for ≥24 months1,§
- 45% of responders (13/29) had onset of response at Cycle 5, the first on-treatment assessment (based on a post hoc analysis)4
- Median time to first confirmed response was 7.9 months (range: 4.1 to 18.8 months)1
85% of patients
(28/33) who completed the treatment phase chose to remain on GOMEKLI for long-term follow-up.2
§Duration of response was assessed based on observed time.1
ǁFour-week cycles of 3 weeks on/1 week off. Treatment phase ends 3 weeks into final cycle.2
¶Partial response corresponds with confirmed overall response of ≥20% reduction in target PN volume from baseline.1
#Stable disease is defined as a <20% increase or a <20% decrease in target PN volume from baseline.2
††Patients who were not evaluable were those for whom no postbaseline volumetric data were collected.4
‡‡Responses were confirmed on a subsequent scan within 2 to 6 months.2
§§Data cutoff was September 20, 2023.2
Discussing GOMEKLI with your patients
The GOMEKLI Patient Brochure can make the ReNeu study data more approachable and easier for you to explain to patients.
Want to learn more about GOMEKLI treatment?
The GOMEKLI Overview Brochure provides an overview of GOMEKLI clinical data for both adult and pediatric patients with NF1-PN.
GOMEKLI safety profile in children
The majority of adverse reactions were mild to moderate and manageable.1
Indication
GOMEKLI (mirdametinib) is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who have symptomatic plexiform neurofibromas (PN) not amenable to complete resection.
Important Safety Information
Warnings and Precautions
Ocular Toxicity: GOMEKLI can cause ocular toxicity including retinal vein occlusion (RVO), retinal pigment epithelium detachment (RPED), and blurred vision. In the adult pooled safety population, ocular toxicity occurred in 28% of patients treated with GOMEKLI: 21% were Grade 1, 5% were Grade 2 and 1.3% were Grade 3. RVO occurred in 2.7%, RPED occurred in 1.3%, and blurred vision occurred in 9% of adult patients. In the pediatric pooled safety population, ocular toxicity occurred in 19% of patients: 17% were Grade 1 and 1.7% were Grade 2. Conduct comprehensive ophthalmic assessments prior to initiating GOMEKLI, at regular intervals during treatment, and to evaluate any new or worsening visual changes such as blurred vision. Continue, withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI as clinically indicated.
Left Ventricular Dysfunction: GOMEKLI can cause left ventricular dysfunction. GOMEKLI has not been studied in patients with a history of clinically significant cardiac disease or LVEF <55% prior to initiation of treatment. In the ReNeu study, decreased LVEF of 10 to <20% occurred in 16% of adult patients treated with GOMEKLI. Five patients (9%) required dose interruption, one patient (1.7%) required a dose reduction, and one patient required permanent discontinuation of GOMEKLI. The median time to first onset of decreased LVEF in adult patients was 70 days. Decreased LVEF of 10 to <20% occurred in 25%, and decreased LVEF of ≥20% occurred in 1.8% of pediatric patients treated with GOMEKLI. One patient (1.8%) required dose interruption of GOMEKLI. The median time to first onset of decreased LVEF in pediatric patients was 132 days. All patients with decreased LVEF were identified during routine echocardiography, and decreased LVEF resolved in 75% of patients. Before initiating GOMEKLI, assess ejection fraction (EF) by echocardiogram. Monitor EF every 3 months during the first year and then as clinically indicated. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity of adverse reaction.
Dermatologic Adverse Reactions: GOMEKLI can cause dermatologic adverse reactions including rash. The most frequent rashes included dermatitis acneiform, rash, eczema, maculo-papular rash and pustular rash. In the pooled adult safety population, rash occurred in 92% of patients treated with GOMEKLI (37% were Grade 2 and 8% were Grade 3) and resulted in permanent discontinuation in 11% of patients. In the pooled pediatric safety population, rash occurred in 72% of patients treated with GOMEKLI (22% were Grade 2 and 3.4% were Grade 3) and resulted in permanent discontinuation in 3.4% of patients. Initiate supportive care at first signs of dermatologic adverse reactions. Withhold, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue GOMEKLI based on severity of adverse reaction.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: GOMEKLI can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of GOMEKLI. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Also advise patients to use effective contraception during treatment with GOMEKLI and for 6 weeks after the last dose (females) or 3 months after the last dose (males).Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (>25%) in adult patients were rash (90%), diarrhea (59%), nausea (52%), musculoskeletal pain (41%), vomiting (38%), and fatigue (29%). Serious adverse reactions occurred in 17% of adult patients who received GOMEKLI. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormality (>2%) was increased creatine phosphokinase.
The most common adverse reactions (>25%) in pediatric patients were rash (73%), diarrhea (55%), musculoskeletal pain (41%), abdominal pain (39%), vomiting (39%), headache (34%), paronychia (32%), left ventricular dysfunction (27%), and nausea (27%). Serious adverse reactions occurred in 14% of pediatric patients who received GOMEKLI. The most common Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities (>2%) were decreased neutrophil count and increased creatine phosphokinase.Use in Specific Populations
Indication
References
- GOMEKLI. Prescribing Information. SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.
- Moertel CL, Hirbe AC, Shuhaiber HH, et al. ReNeu: a pivotal, phase IIb trial of mirdametinib in adults and children with symptomatic neurofibromatosis type 1-associated plexiform neurofibroma. J Clin Oncol. 2025;43(6):716-729.
- Gershon T, Moertel C, McNall-Knapp RY, et al. Pivotal, phase 2b ReNeu trial of mirdametinib in children and adults with neurofibromatosis type 1-associated plexiform neurofibroma (NF1-PN): a spotlight on patients achieving deep response. Poster presented at: 29th Annual Meeting of the Society for Neuro-Oncology; November 21-24, 2024; Houston, TX.
- Data on file: SpringWorks Therapeutics, Inc.
- Hirbe AC, Moertel CL, Shuhaiber HH, et al. Update from the long-term follow-up (LTFU) phase of ReNeu: a pivotal phase 2b trial of mirdametinib in children and adults with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)-associated symptomatic plexiform neurofibroma (PN). Presented at: 2025 Global NF Conference; June 21-24, 2025; Washington, DC.